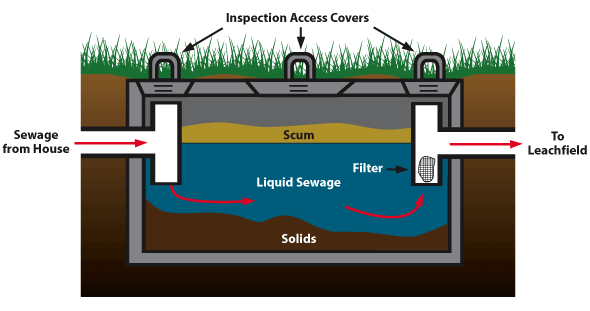
I.T.T.E sep!c tanks was originally designed to serve as a se0ling basin to separate scum and grit from the liquid. The effluent from the tank then was sent to a sewer or the soil for disposal
The clarification function of the tank was known, but the biological processes that partially digested sewage were discovered it is found that the organic solids in the wastewater decomposed if they stayed in the tank long enough. Therefore, the septic tank is designed to accomplish two tasks: (1) Clarification , (2) Treatment.

Clarification is a function of the detention time and the water extraction method. Solids settle out of the water based on size and specific gravity.Smaller lighter particles take longer to settle than heavier particles.Clarification also includes the removal of fats, oils and greases, which float to the surface along with soapsuds and “scum”.The variables of a septic tank are: size, shape, number of chambers, number and style of baffles and gas venting provisions.
Efficient clarification takes time to complete because fats, oils, greases, and suspended solids travel
slowly in water and may require hours to either float to the top or settle to the bottom.
The shape of the tank must be designed to maximize the detention time of the wastewater.
Surface area is more critical for settle ability than depth, so a shallow, wide tank is preferable to a deep,
narrow tank if both have the same volume capacity. Shallow tanks are also easier to transport and install
and poses less of a safety risk because the content level of the tank is not much deeper than the height
of an average person.
An improperly configured tank will allow wastewater to “short-circuit” through the tank to the outlet.
Short-circuiting can allow solids to migrate to the absorption field if the wastewater is not given sufficient
time for the solids to settle out.